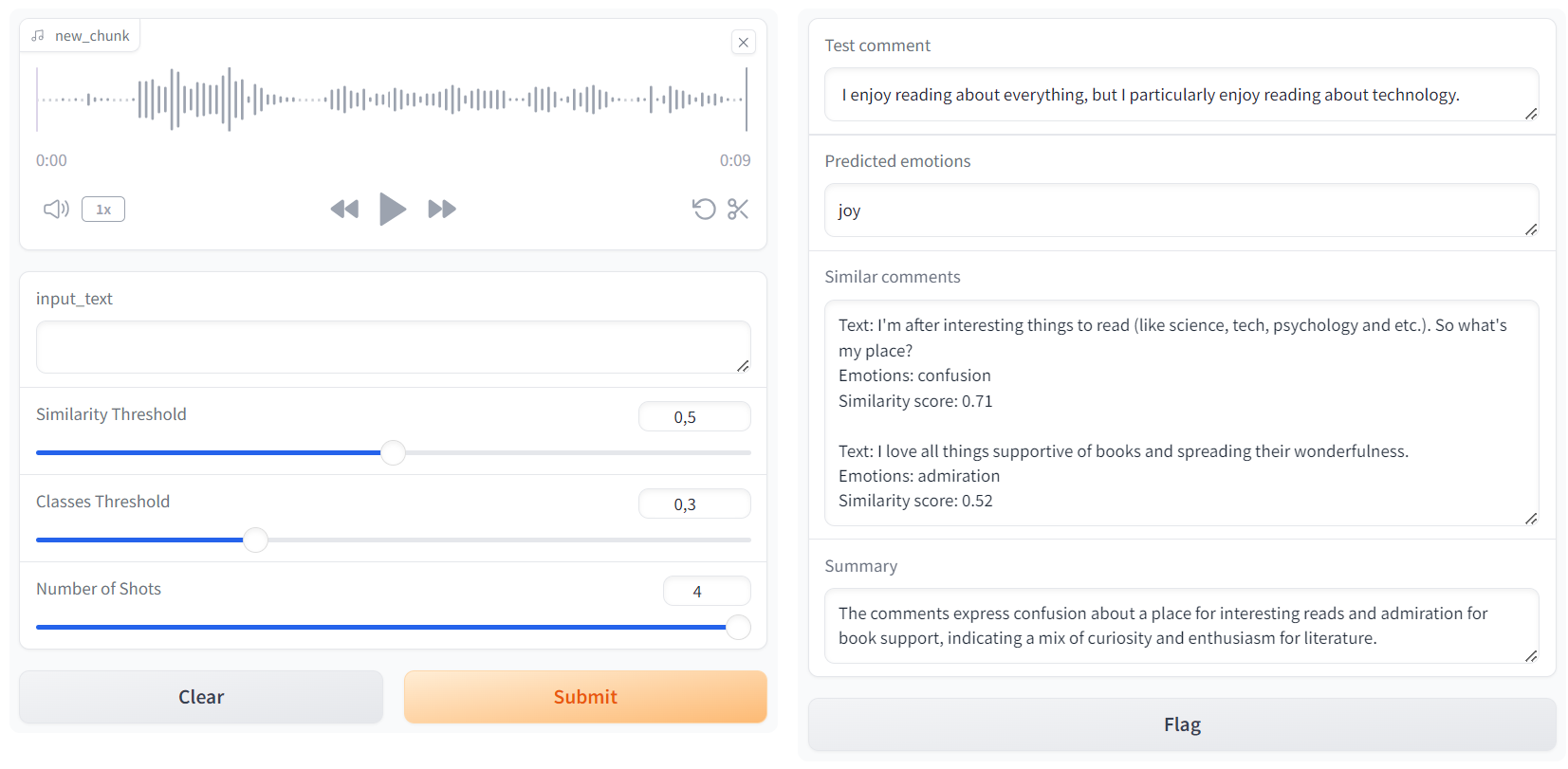
Sentiment Analysis and RAG with LLMs and Transformers
Sentiment analysis and Retrieval Augmented Generation leveraging BERT, Hugging Face transformers, Mistral LLMs and ASR.
This project focuses on implementing a comprehensive Natural Language Processing (NLP) pipeline for sentiment analysis and etrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) using state-of-the-art transformer models. The system accepts text or audio input, converts the audio to text, predicts sentiment labels with a fine-tuned BERT text classification model, retrieves similar comments using cosine similarity from Hugging Face encodings, and generates summaries using a Mistral Face large language model (LLM). The integration of these components showcases advanced NLP techniques, including sentiment analysis, contextual embeddings, and prompt engineering, within a seamless and interactive web interface.
Sentiment Analysis with BERT’s Fine Tuning
The core of the sentiment analysis component is based on the BERT large uncased emotions model. Fine-tuning this model involved extensive parameter tuning to optimize the precision, recall, and F1 score. Various configurations of maximum sequence length, batch size, learning rate, and epochs were tested to identify the best performing setup. The following table summarizes the results of tuning different hyperparameters for the BERT text classification model. The evaluation metrics include precision, recall, and F1 score for each configuration:
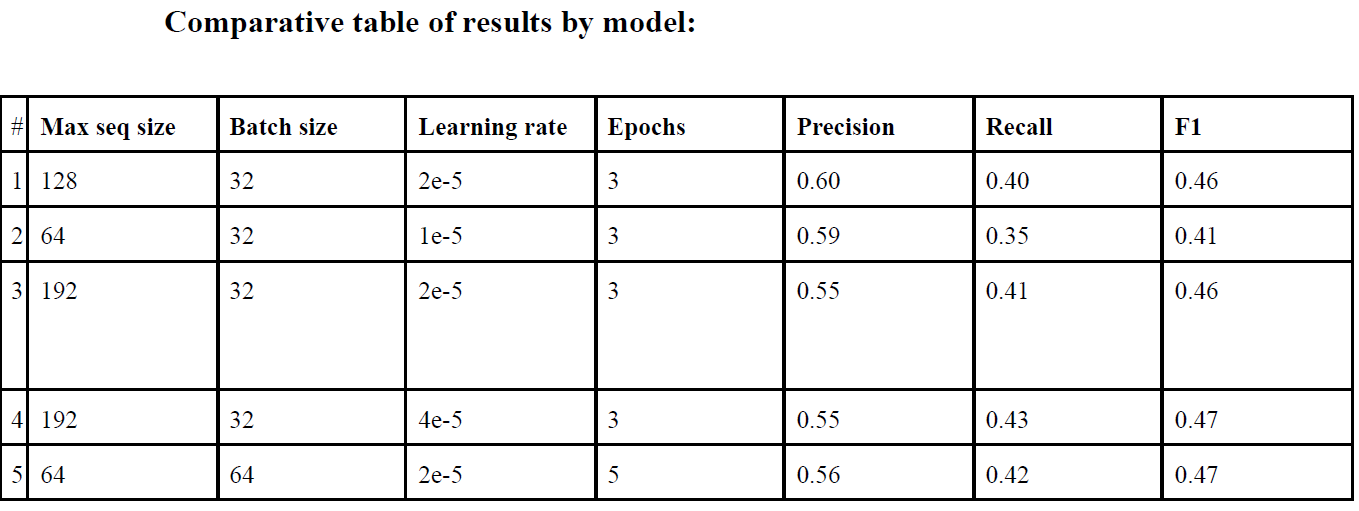
The optimal configuration, highlighted by a combination of high precision, recall, and F1 score, was used to fine-tune the BERT model, enhancing its performance for the sentiment analysis task. The optimal threshold for the classes labeling was between 0.2 and 0.3, as highlighted in the report.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
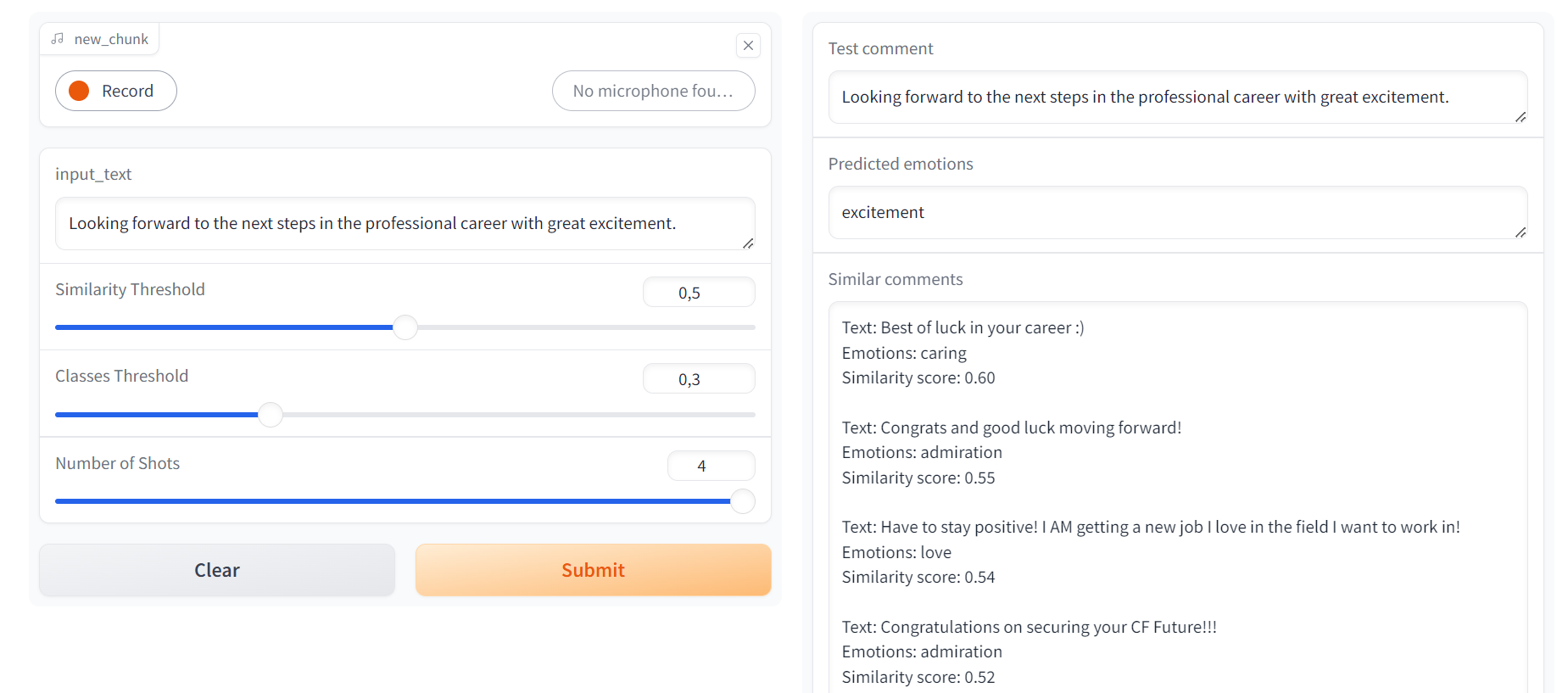
The Retrieval-Augmented Generation process in this project involves using a sentence transformer model from Hugging Face, specifically the all-MiniLM-L6-v2, to encode the comments. The encoded comments are then compared using cosine similarity to retrieve the most similar ones. The optimal threshold for cosine similarity was found to be around 0.5.
For complex or lengthy input comments, where the likelihood of finding an exact match in the dataset is lower, a lower threshold can be employed to ensure some relevant outputs are retrieved. Conversely, for very short and straightforward sentences, a higher threshold can be beneficial to filter out only those comments that are strictly similar to the input, thus maintaining high precision. This dynamic adjustment of the threshold based on the input characteristics enhances the robustness and flexibility of the retrieval-augmented generation process.
Summary Generation with Mistral’s LLM
For the summary generation component, we used a large language model (LLM) to generate summaries from the selected comments based on our similarity threshold and the chosen shot strategy. Prompt engineering played a crucial role in this process. We implemented various prompt strategies, including zero-shot, one-shot, two-shot, three-shot, and four-shot prompts, to determine which approach yielded the best results.
The zero-shot prompt used was:
Summarize shortly the comments provided above.
Describe general emotions.
The few-shot prompt was more structured:
● You are a summarizer bot.
● Your task is to given a group of comments you should return a general summary of the group of comments.
● You must not summarize each comment individually, you should summarize them as a whole.
● Describe general emotions.
● Do not provide additional explanations or notes, just the summary.
● Do not use more than 60 words.
● The group of comments is inside <<<>>>.
● Here are some examples: ...
We experimented with two large language models: Mistral 7B and Mixtral 8x7B. The Mixtral 8x7B model, which employs a sparse mixture of experts (MoEs) architecture, combines outputs from eight different experts efficiently, making both training and inference highly effective. We observed that Mixtral 8x7B outperformed Mistral 7B in the zero-shot prompt scenario, likely due to the greater flexibility and adaptability required in zero-shot tasks. However, with few-shot prompts, the additional examples provided sufficient orientation, leading to similar performance levels for both models.
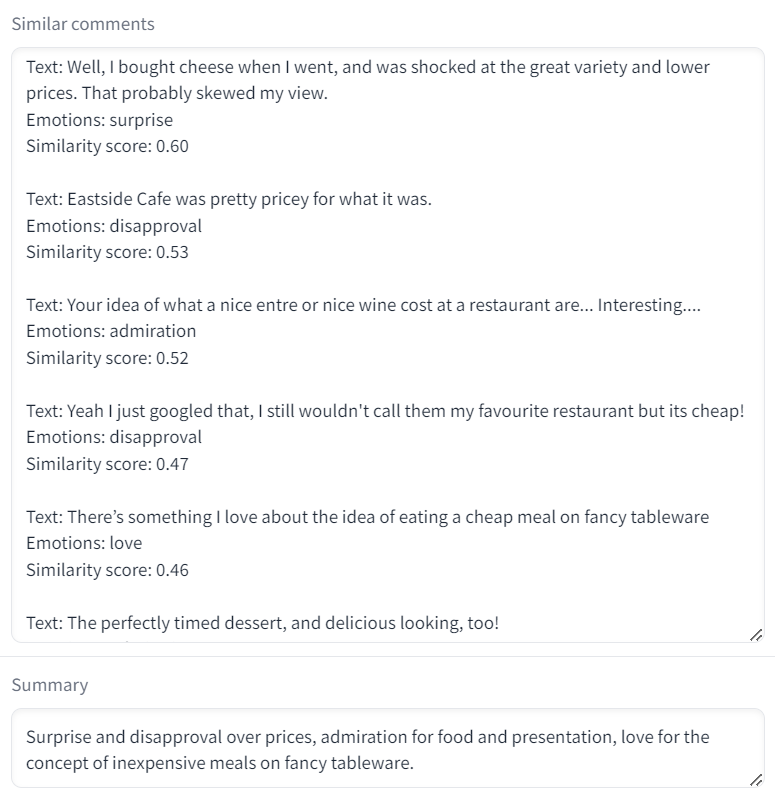

The four-shot prompt strategy consistently yielded the best results. Our report concluded that structured and refined prompts significantly outperformed the original, unstructured prompts. Adding detailed instructions, a clear sequence of actions, and delimiters followed best practices for prompting, thereby achieving the desired output more effectively. The use of structured examples improved the models’ ability to capture nuanced emotional tones and specific contexts, highlighting the importance of precise prompt design in optimizing LLM performance for summarization tasks.
Automatic Speech Recognition
The project also incorporates Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) using OpenAI’s Whisper ASR model. This allows the system to accept both audio and text inputs, converting audio to text with high accuracy before processing it for sentiment analysis, comment retrieval, and summarization. This functionality enhances the versatility and accessibility of the application, enabling users to interact with the system through multiple input modalities.