Anomaly Detection Hierarchical Deep Learning Model
Hierarchical Deep Learning model for anomaly detection in water consumption data, presented with an interactive web visualization.
Water distribution networks in urban environments face the crucial challenge of detecting anomalies like leaks, excessive consumption, or meter errors. These anomalies often go unnoticed until significant water loss occurs. This project tackles this critical issue by presenting a novel, adaptable deep learning meta-model specifically designed for anomaly detection in water meter data.
Paper
Leveraging Deep Learning for Time Series
Traditional machine learning methods like SVMs and Isolation Forests often struggle with large, time-dependent datasets like water consumption data. Deep learning methods, on the other hand, have shown promising results in anomaly detection tasks. Transformers, in particular, excel at identifying complex patterns in sequential data, making them a strong candidate for this application (Tuli, Casale, & Jennings, 2022).
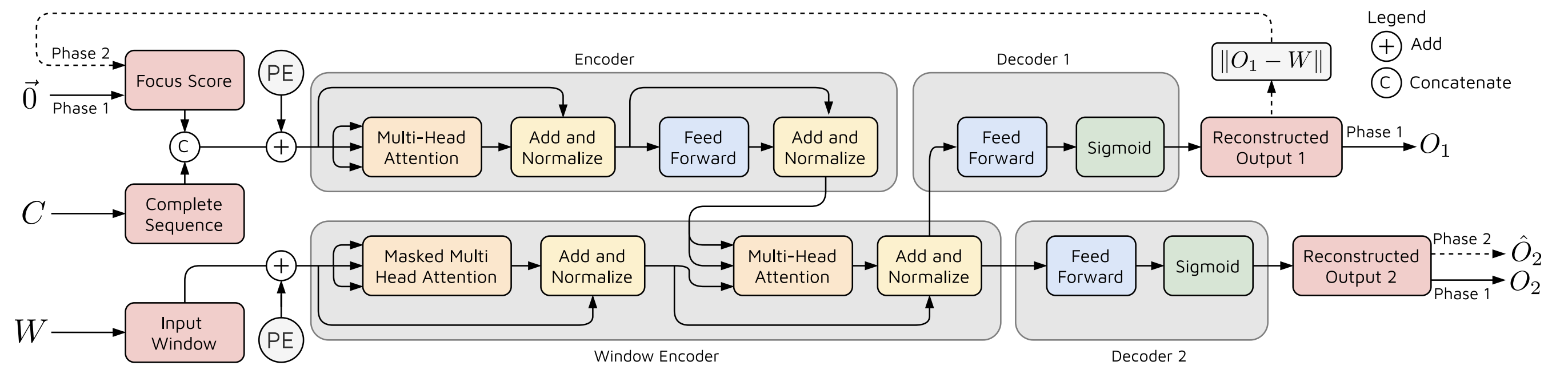
Our model, leveraging the power of LSTMs and Transformers, effectively captures sequential consumption patterns and identifies deviations from normal behavior. This enables early detection of anomalies, potentially leading to significant cost savings for both water companies and consumers, while promoting sustainable water usage.
Multi-Stage Hierarchical Architecture
The core of this project lies in its hierarchical deep learning architecture, specifically designed for anomaly detection in water consumption data. This multi-stage training approach fosters specialization in the later stages while preserving valuable generalizations learned earlier.
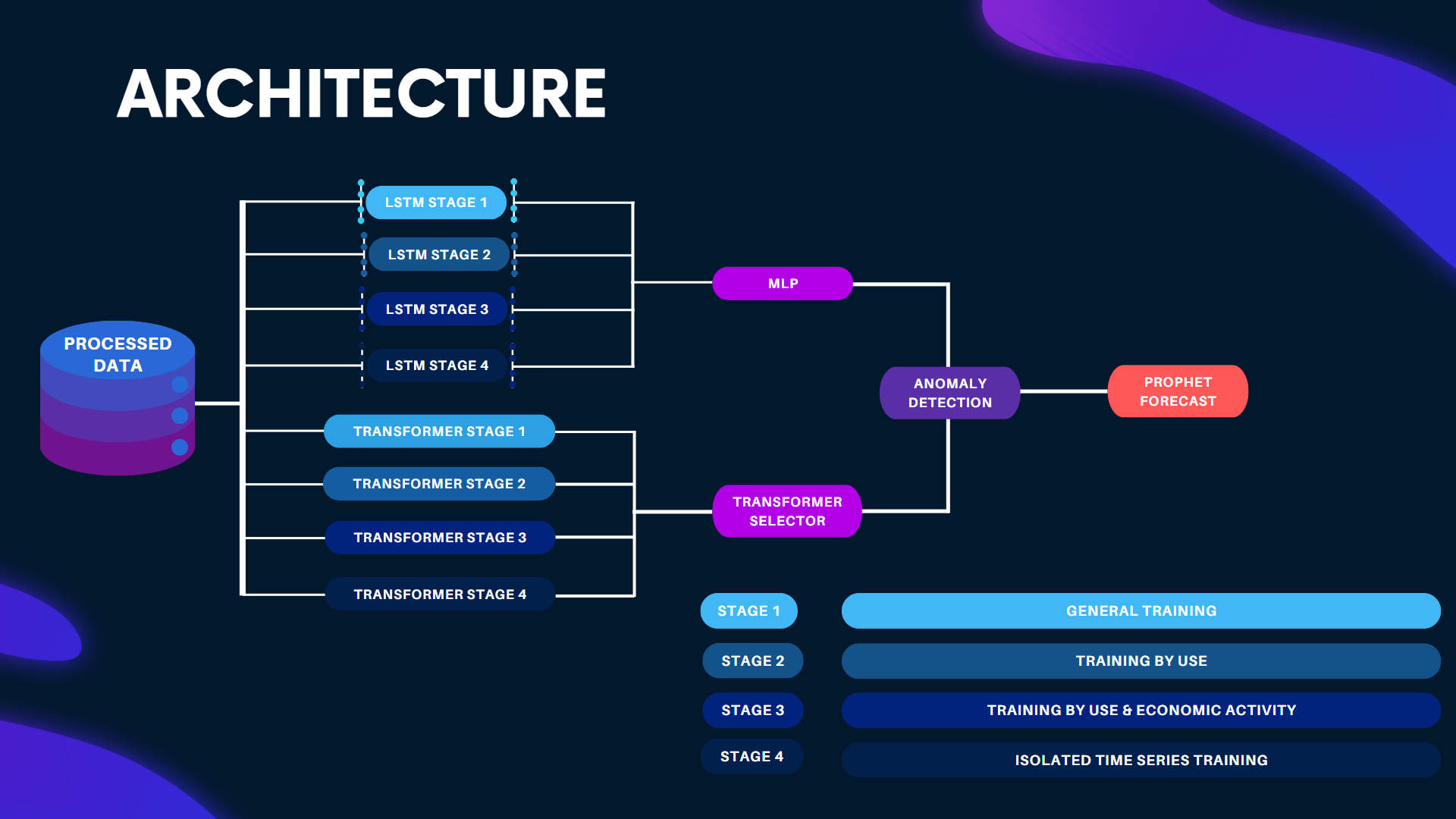
This balance between adaptability to specific data patterns and overall robustness in anomaly detection is achieved through the integration of three key components:
-
TranAD: This transformer-based model excels at identifying deviations in time series data. It undergoes a two-phase adversarial training process to capture both short-term trends and long-term dependencies within the data.
-
Multi-LSTM: This advanced LSTM architecture tackles the challenge of analyzing data across multiple temporal windows simultaneously. This capability is crucial for capturing complex patterns at various time scales, enhancing the model’s accuracy and robustness. Unlike conventional LSTMs, our Multi-LSTM allows for parameterization of both the number of LSTMs and the size of their temporal windows, enabling greater adaptability to diverse data.
-
Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP): This final component acts as a decision layer, evaluating and combining the outputs from the previous stages. By integrating the general insights from earlier training stages with the specialized knowledge of later stages, the MLP provides a single, highly accurate prediction while avoiding overfitting.
The synergy between these components lies at the heart of the model’s power. The precise anomaly detection capabilities of TranAD are complemented by the Multi-LSTM’s ability to handle complex temporal dependencies. Finally, the MLP effectively combines these strengths, leading to a robust and versatile solution for anomaly detection in water consumption data.
- Prophet: As an additional, external part of the model, we integrated Meta’s Prophet forecasting model in order to forecast future water consumption. In this way, we can both detect anomalies and have a robust predictive tool for consumption that can improve data-based decisions on the user side.
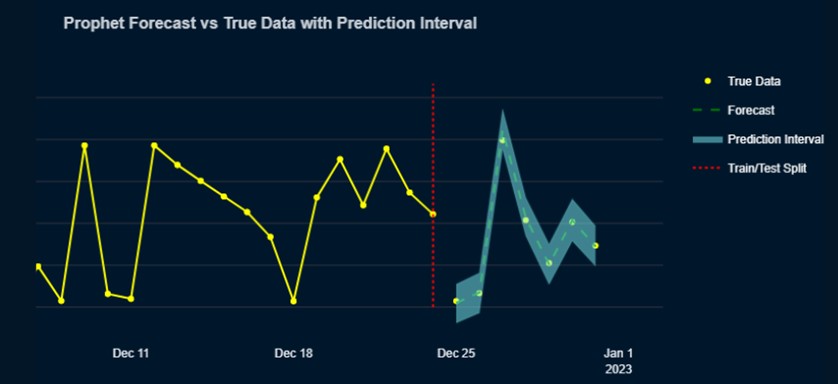
Interactive Anomaly Visualization
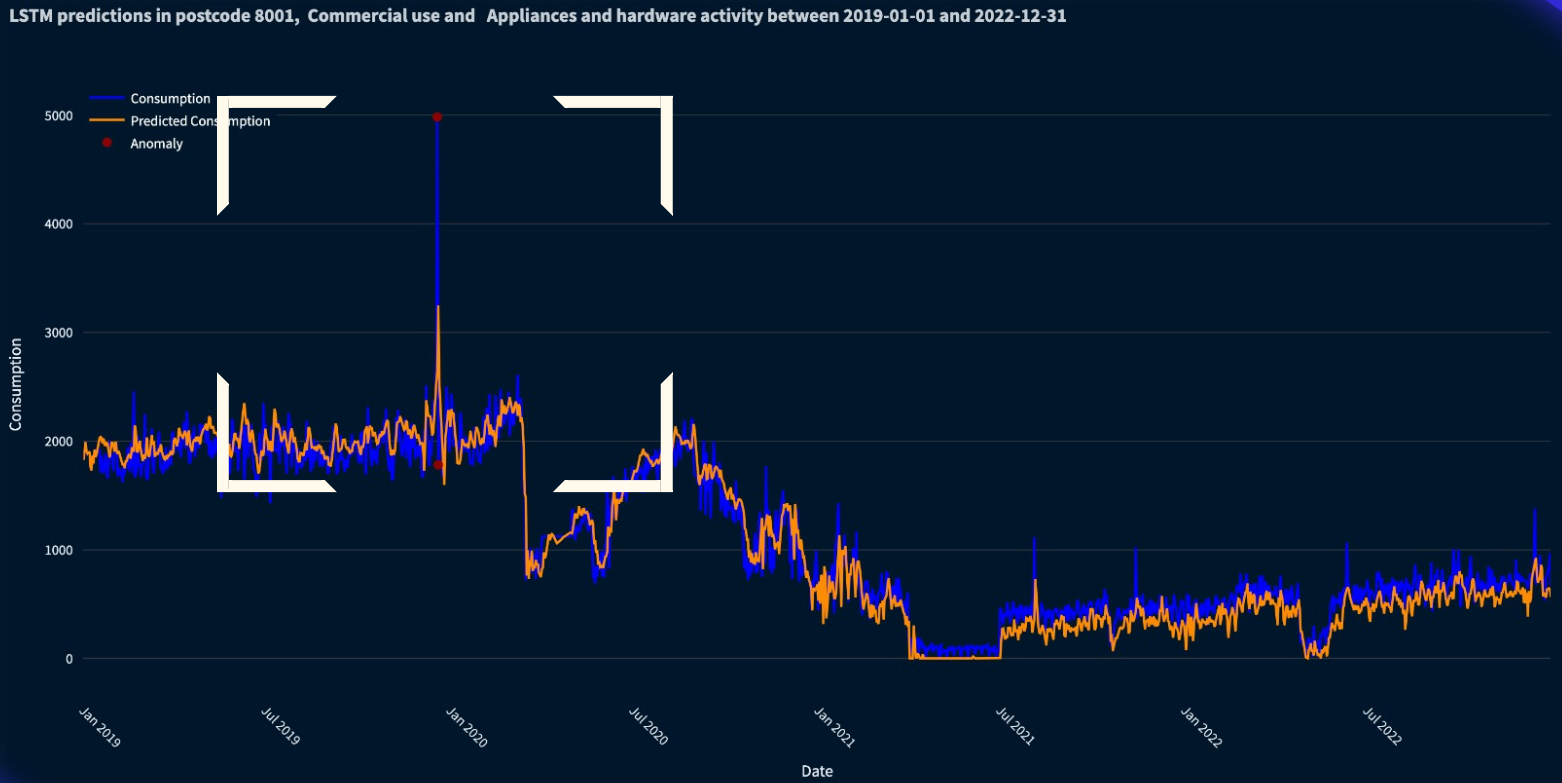
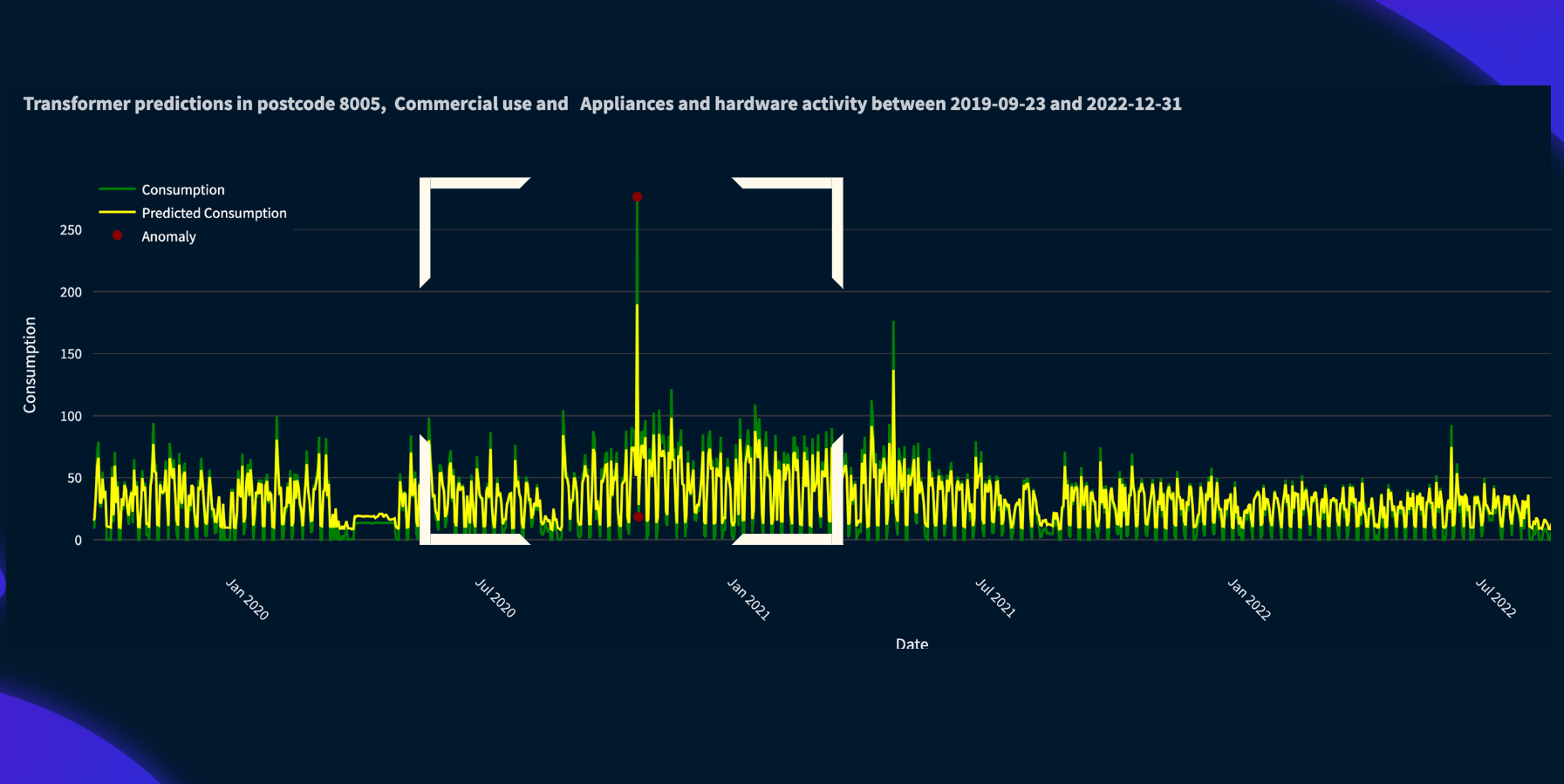
Our project is complemented by a comprehensive web application designed for user-friendly exploration of water consumption patterns and anomalies. This intuitive interface allows visualization of multiple time series simultaneously, aiding in informed decision-making. The application offers in-depth analysis of anomalous data, including visualizations of model predictions alongside actual consumption values, highlighting anomaly points. Furthermore, it empowers users to explore future consumption predictions and geographically visualize anomalies across different areas. By integrating socioeconomic indicators, the web application facilitates strategic decision-making for optimized water resource management.
References
Guha, S., Mishra, N., Roy, G., & Schrijvers, O. (2016, June). Robust random cut forest based anomaly detection on streams. In International conference on machine learning (pp. 2712-2721). PMLR.
Li, K. L., Huang, H. K., Tian, S. F., & Xu, W. (2003, November). Improving one-class SVM for anomaly detection. In Proceedings of the 2003 international conference on machine learning and cybernetics (IEEE Cat. No. 03EX693) (Vol. 5, pp. 3077-3081). IEEE.
Lin, S., Clark, R., Birke, R., Schönborn, S., Trigoni, N., & Roberts, S. (2020, May). Anomaly detection for time series using vae-lstm hybrid model. In ICASSP 2020-2020 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (pp. 4322-4326). Ieee.
Liu, F. T., Ting, K. M., & Zhou, Z. H. (2008, December). Isolation forest. In 2008 eighth ieee international conference on data mining (pp. 413-422). IEEE.
Pang, G., Shen, C., Cao, L., & Hengel, A. V. D. (2021). Deep learning for anomaly detection: A review. ACM computing surveys (CSUR), 54(2), 1-38.
Su, Y., Zhao, Y., Niu, C., Liu, R., Sun, W., & Pei, D. (2019, July). Robust anomaly detection for multivariate time series through stochastic recurrent neural network. In Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery & data mining (pp. 2828-2837).
Tuli, S., Casale, G., & Jennings, N. R. (2022). Tranad: Deep transformer networks for anomaly detection in multivariate time series data. arXiv preprint arXiv:2201.07284.
Vaswani, A., Shazeer, N., Parmar, N., Uszkoreit, J., Jones, L., Gomez, A. N., … & Polosukhin, I. (2017). Attention is all you need. Advances in neural information processing systems, 30.